Since 1985, our team of experienced physicians, respiratory therapists and exercise physiologists at Exeter Hampton Diagnostics have provided the tri-state area with the most thorough and comprehensive testing. Our state of the art physiology lab is conveniently located in the North Hampton office of Center for Asthma, Allergy and Respiratory Disease. Testing performed at EHD helps our specialists make an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan to meet patient’s individual needs.
Our services include:
- Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) is a group of tests designed to measure how well the lungs take in and release air and how well gases such as oxygen move into the body?s circulation. A PFT is done to: diagnose certain types of disease (such as asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema), find the cause of shortness of breath, assess the effect of medications and measure progress in disease treatment.
There are 4 different tests to measure the function of your lungs: spirometry, forced inhalation or exhalation, lung volume measurement, and diffusion capacity.
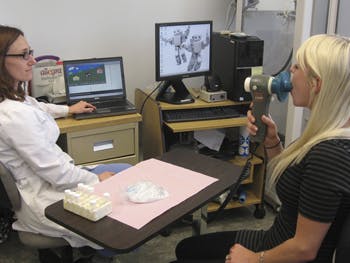
- Spirometry measures airflow. While you are sitting, you breathe into a mouthpiece connected to an instrument called a spirometer. The spirometer records the amount and rate of air that you breathe in and out over a period of time.
- Forced Inhalation/Exhalation is a measurement test required after a deep breath. Sometimes you will be asked to inhale a substance or medicine to see how it affects your test results.
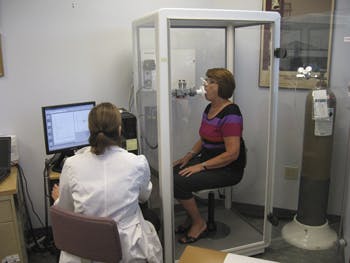
- Lung Volume Measurement is most accurate when you sit in a clear, sealed booth (called a body box or body plethysmography) and breathe in and out of a mouthpiece. Pressure changes inside the body box help determine lung volume.
- Diffusion Capacity Measurement is taken when you breathe in a harmless gas (tracer gas) for a very brief time. The concentration of the gas in the air you breathe out is then measured. The difference in the amount of gas inhaled versus exhaled measures how effectively gas moves from the lungs into the blood. This test estimates how well oxygen travels from the air into the bloodstream.
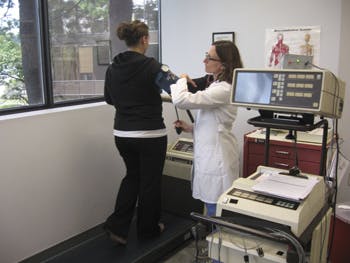
- Bronchial Provocation Testing evaluates how sensitive your lung airways are, and is used to diagnose hyperactive airway disease (asthma). The test requires you to breathe increasing dosages of a bronchoconstrictor called Methacholine. Your spirometry (lung volume) is measured before and after each dose of methacholine to see what changes there are in your breathing.
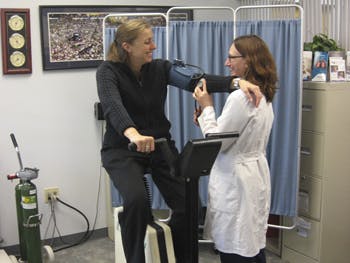
- Cardiopulmonary Stress Testing is an exercise test that uses a treadmill or stationary bicycle (ergometer), and state-of-the-art computer equipment for the purpose of evaluating cardiac/pulmonary disease. We measure how well your lungs work while exercising, and we monitor your heart response, oxygen concentration and blood pressure throughout the test. This test can help identify exercise-induced asthma as well as exercise tolerance.
- Body Composition Analysis (Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis) is a test to accurately access body composition, and body fat in particular. BIA measures the impedance or opposition to the flow of an electric current through the body fluids contained in the lean and fat tissue. Impedance is low in lean tissue and high in fat tissue. Fat mass is calculated as the difference between body weight and lean body mass.
- Lipid Profile and Glucose Testing